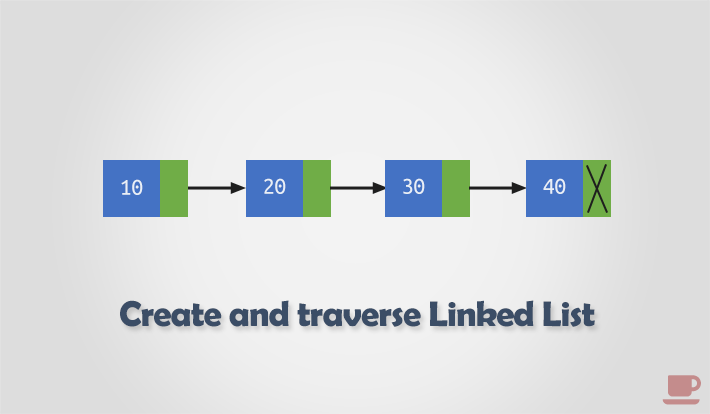
Linked list creation and traversal is the stepping stone in data structures. In this article, I will explain how to create and traverse a linked list in C programming. I will explain step by step process to create and traverse a linked list of n nodes and display its elements.
Write a C program to implement Singly linked list data structure. C program to create a linked list and display elements of linked list.
Required knowledge
Functions, Structures, Pointers, Dynamic Memory Allocation
How to create and traverse a linked list?
In previous article we discussed about singly linked list data structure, its need and advantages. Here we will learn to create and traverse a linked list in C program.
How to create a linked list?
Step by step descriptive logic to create a linked list.
- The first step of creating linked list of n nodes starts from defining node structure. We need a custom type to store our data and location of next linked node. Let us define our custom node structure
struct node { int data; struct node *next; };Where data is the data you want to store in list. *next is pointer to the same structure type. The *next will store location of next node if exists otherwise
NULL.Note: The node structure may vary based on your requirement. You can also have user defined types as node data section.
- Declare a pointer to node type variable to store link of first node of linked list. Say
struct node *head;.Note: You can also declare variable of node type along with node structure definition.
- Input number of nodes to create from user, store it in some variable say n.
- Declare two more helper variable of node type, say
struct node *newNode, *temp;. - If
n > 0then, create our first node i.e. head node. Use dynamic memory allocation to allocate memory for a node. Sayhead = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));. - If there is no memory to allocate for head node i.e.
head == NULL. Then print some error message and terminate program, otherwise move to below step. - Input data from user and assign to head using
head->data = data;. - At first head node points to
NULL. Hence, assignhead->next = NULL;. - Now, we are done with head node we should move to creation of other nodes. Copy reference of head to some other temporary variable, say
temp = head;. We will use temp to store reference of previous node. - Allocate memory and assign memory reference to newNode, say
newNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(node));. - If memory got allocated successfully then read data from user and assign to data section of new node. Say
newNode->data = data;. - Make sure new node points to
NULL. - Now link previous node with newly created node i.e.
temp->next = newNode;. - Make current node as previous node using
temp = temp->next;. - Repeat step 10-14 for remaining
n - 2other nodes.
How to traverse a linked list?
Step by step descriptive logic to traverse a linked list.
- Create a temporary variable for traversing. Assign reference of head node to it, say
temp = head. - Repeat below step till
temp != NULL. temp->datacontains the current node data. You can print it or can perform some calculation on it.- Once done, move to next node using
temp = temp->next;. - Go back to 2nd step.
Example program to create and traverse a linked list
/**
* C program to create and traverse a Linked List
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* Structure of a node */
struct node {
int data; // Data
struct node *next; // Address
}*head;
/*
* Functions to create and display list
*/
void createList(int n);
void traverseList();
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter the total number of nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
createList(n);
printf("\nData in the list \n");
traverseList();
return 0;
}
/*
* Create a list of n nodes
*/
void createList(int n)
{
struct node *newNode, *temp;
int data, i;
head = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Terminate if memory not allocated
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to allocate memory.");
exit(0);
}
// Input data of node from the user
printf("Enter the data of node 1: ");
scanf("%d", &data);
head->data = data; // Link data field with data
head->next = NULL; // Link address field to NULL
// Create n - 1 nodes and add to list
temp = head;
for(i=2; i<=n; i++)
{
newNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* If memory is not allocated for newNode */
if(newNode == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to allocate memory.");
break;
}
printf("Enter the data of node %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", &data);
newNode->data = data; // Link data field of newNode
newNode->next = NULL; // Make sure new node points to NULL
temp->next = newNode; // Link previous node with newNode
temp = temp->next; // Make current node as previous node
}
}
/*
* Display entire list
*/
void traverseList()
{
struct node *temp;
// Return if list is empty
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("List is empty.");
return;
}
temp = head;
while(temp != NULL)
{
printf("Data = %d\n", temp->data); // Print data of current node
temp = temp->next; // Move to next node
}
}Enter the total number of nodes: 5 Enter the data of node 1: 10 Enter the data of node 2: 20 Enter the data of node 3: 30 Enter the data of node 4: 40 Enter the data of node 5: 50 Data in the list Data = 10 Data = 20 Data = 30 Data = 40 Data = 50
Happy coding 😉
