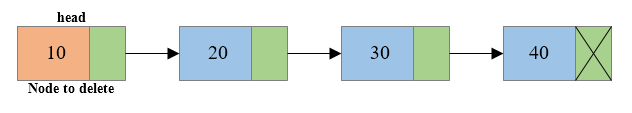
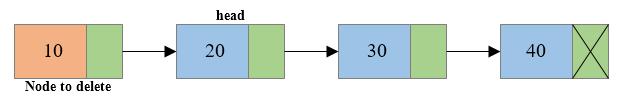
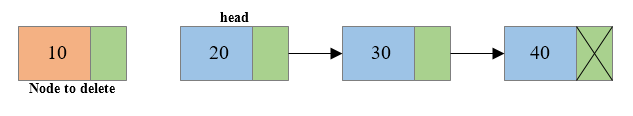
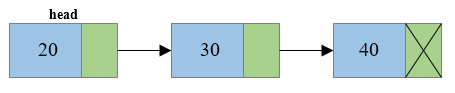
Write a C program to create a singly linked list of n nodes and delete the first node or beginning node of the linked list. How to delete first node from singly linked list in C language. Algorithm to delete first node from singly linked list in C. Steps to delete first node from singly linked list.
Required knowledge
Basic C programming, Functions, Singly Linked List, Dynamic memory allocation
Algorithm to delete first node from Singly Linked List
Algorithm to delete first node of Singly Linked List
%%Input: head of the linked list
Begin:
If (head != NULL) then
toDelete ← head
head ← head.next
unalloc (toDelete)
End if
EndSteps to delete first node from Singly Linked List
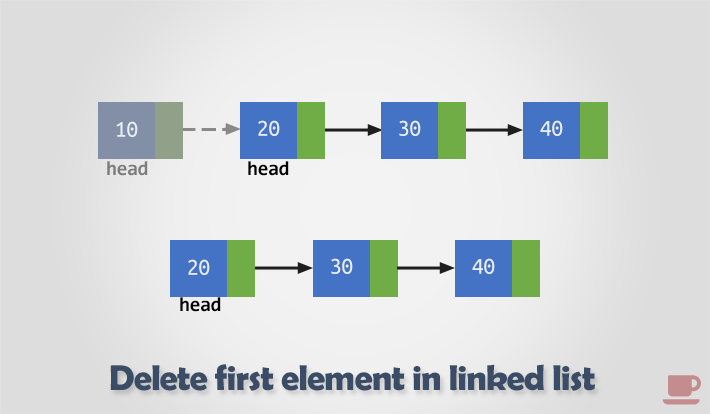
- Copy the address of first node i.e. head node to some temp variable say toDelete.

- Move the head to the second node of the linked list i.e. head = head->next.

- Disconnect the connection of first node to second node.

- Free the memory occupied by the first node.

Program to delete first node of Singly Linked List
/**
* C program to delete first node from Singly Linked List
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* Structure of a node */
struct node {
int data; // Data
struct node *next; // Address
}*head;
void createList(int n);
void deleteFirstNode();
void displayList();
int main()
{
int n, choice;
/*
* Create a singly linked list of n nodes
*/
printf("Enter the total number of nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
createList(n);
printf("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
printf("\nPress 1 to delete first node: ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
/* Delete first node from list */
if(choice == 1)
deleteFirstNode();
printf("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
return 0;
}
/*
* Create a list of n nodes
*/
void createList(int n)
{
struct node *newNode, *temp;
int data, i;
head = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/*
* If unable to allocate memory for head node
*/
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to allocate memory.");
}
else
{
/*
* In data of node from the user
*/
printf("Enter the data of node 1: ");
scanf("%d", &data);
head->data = data; // Link the data field with data
head->next = NULL; // Link the address field to NULL
temp = head;
/*
* Create n nodes and adds to linked list
*/
for(i=2; i<=n; i++)
{
newNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* If memory is not allocated for newNode */
if(newNode == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to allocate memory.");
break;
}
else
{
printf("Enter the data of node %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", &data);
newNode->data = data; // Link the data field of newNode with data
newNode->next = NULL; // Link the address field of newNode with NULL
temp->next = newNode; // Link previous node i.e. temp to the newNode
temp = temp->next;
}
}
printf("SINGLY LINKED LIST CREATED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
}
}
/*
* Deletes the first node of the linked list
*/
void deleteFirstNode()
{
struct node *toDelete;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("List is already empty.");
}
else
{
toDelete = head;
head = head->next;
printf("\nData deleted = %d\n", toDelete->data);
/* Clears the memory occupied by first node*/
free(toDelete);
printf("SUCCESSFULLY DELETED FIRST NODE FROM LIST\n");
}
}
/*
* Displays the entire list
*/
void displayList()
{
struct node *temp;
/*
* If the list is empty i.e. head = NULL
*/
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("List is empty.");
}
else
{
temp = head;
while(temp != NULL)
{
printf("Data = %d\n", temp->data); // Print data of current node
temp = temp->next; // Move to next node
}
}
}Enter the total number of nodes: 5 Enter the data of node 1: 10 Enter the data of node 2: 20 Enter the data of node 3: 30 Enter the data of node 4: 40 Enter the data of node 5: 50 SINGLY LINKED LIST CREATED SUCCESSFULLY Data in the list Data = 10 Data = 20 Data = 30 Data = 40 Data = 50 Press 1 to delete first node: 1 Data deleted = 10 SUCCESSFULLY DELETED FIRST NODE FROM LIST Data in the list Data = 20 Data = 30 Data = 40 Data = 50