pwd stands for Print Working Directory. It prints the complete absolute path of current directory you are in.
While working with Linux files and directories, you move around from one directory to another. Anytime if you want to know in which directory you are in then, pwd command tells you that.
Syntax
pwd [-LP]
Where L and P are optional options.
Options
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
-L | Displays the logical path of current working directory. This logical path includes the symbolic link path of current working directory. This is the default option, if no options specified. |
-P | Displays the physical path of current working directory after resolving symbolic links. It shows the full pathname without symbolic link of the current working directory. |
Note: When no option is specified with the command pwd , it automatically considers -L into action.
Examples
Let us try some fun with pwd command and see where we exist.
To know current working directory just hit either pwd or pwd -L in any directory.
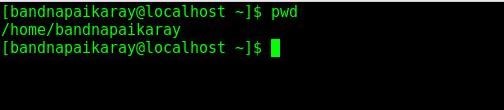
pwd or pwd -L both are equivalent.
Let us now try pwd with -P option. Since it displays the physical path of current working directory after resolving symbolic links. Hence we need to create a symbolic link to test.
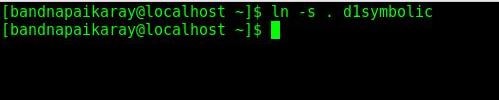
- Create a symbolic link of current directory, hit
ln -s . d1symbolic
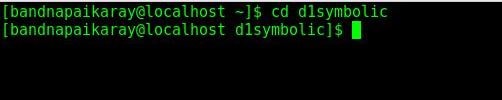
- Navigate to the newly created symbolic link, hit
cd d1symbolic.
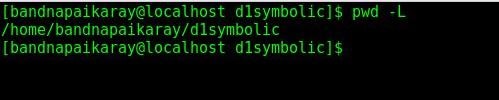
- Now if you do
pwdorpwd -L, the output will be the full pathname without resolving symbolic link.
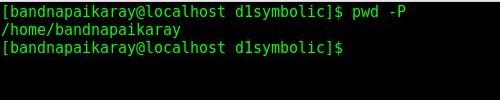
- However, if you do
pwd -Pthen it will print current working directory path after resolving symbolic link.
Feel free to drop you comments suggestions in comments section.
Happy coding ??