Multi-dimensional array is an array of array or more precisely collection of array. Unlike one-dimensional array, multi-dimensional array stores collection of array.
Let us revise the concept of dimension.
- One-dimensional array : Collection of data/values.
- Two-dimensional array : Collection of one-dimensional array.
- Three-dimensional array : Collection of two-dimensional array.
- N-dimensional array : Collection of
N-1dimensional array.
We can declare array with any dimension. However, two-dimensional array is most popular and widely used to solve many mathematical problems.
Note: Whether it is one, two or N-dimensional array. All array elements are stored sequentially in memory.
Two-dimensional array
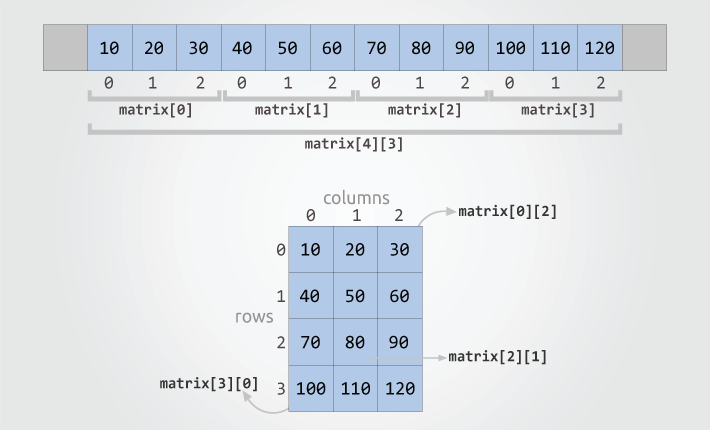
Two-dimensional array is a collection of one-dimensional array. Two-dimensional array has special significance than other array types. You can logically represent a two-dimensional array as a matrix. Any matrix problem can be converted easily to a two-dimensional array.
Syntax to declare two-dimensional arraytype array_name[row-size][col-size];
type is a valid C data type.array_name is a valid C identifier that denotes name of the array.row-size is a constant that specifies matrix row size.col-size is also a constant that specifies column size. col-size is optional when initializing array during its declaration.
Example to declare two-dimensional arrayint matrix[3][4];
type array_name[row-size][col-size];type is a valid C data type.array_name is a valid C identifier that denotes name of the array.row-size is a constant that specifies matrix row size.col-size is also a constant that specifies column size. col-size is optional when initializing array during its declaration.int matrix[3][4];The above statement declares a two-dimensional integer array of size 3×4 i.e. 3 rows and 4 columns (in terms of matrix).
How to initialize two-dimensional array
You can initialize a two-dimensional array in any of the given form.
int matrix[4][3] = {
{10, 20, 30}, // Initializes matrix[0]
{40, 50, 60}, // Initializes matrix[1]
{70, 80, 90}, // Initializes matrix[2]
{100, 110, 120} // Initializes matrix[3]
};If you have mentioned row and column size specifically then curly braces for each row inside array initialization is optional. Hence, you can write the above initialization as.
int matrix[4][3] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120};Note: Be cautious while using the above approach to initialize. You must explicitly provide row and column size. Otherwise C compiler will generate compilation errors.
Array column size is optional if specifying individual rows within pair of curly braces.
int matrix[4][] = {
{10, 20, 30}, // Initializes matrix[0]
{40, 50, 60}, // Initializes matrix[1]
{70, 80, 90}, // Initializes matrix[2]
{100, 110, 120} // Initializes matrix[3]
};There are several ways to initialize a two-dimensional array. It depends on programmers how they initialize. However, the first approach is considered as standard to initialize a two-dimensional array.
How to access two-dimensional array
Two-dimensional array uses two index values to access a particular element. Where first index specifies row and second specifies column to access.
Example to access two-dimensional array
matrix[0][0] = 10; // Assign 10 to first element of first row
matrix[0][1] = 20; // Assign 20 to second element of first row
matrix[1][2] = 60; // Assign 60 to third element of second row
matrix[3][0] = 100; // Assign 100 to first element of fourth rowSince array indexes are integer value, hence you can also wire a loop to access two-dimensional array. Two-dimensional array needs two index values to access any array element. Therefore you need two loops. One outer loop to access for each row of the matrix, second loop for each column of the matrix.
// Runs 4 times iterating through each row
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
// Runs 3 times for each row.
for(j=0; j<3; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &matrix[i][j]);
}
}Example program to use two-dimensional array
Write a C program to declare a two-dimensional array of size 4×3. Read values in each element of array from user and display values of all elements.
/**
* C program to input and display two-dimensional array
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define ROW_SIZE 4 // Define constant row size
#define COL_SIZE 3 // Define constant column size
int main()
{
int matrix[ROW_SIZE][COL_SIZE];
int row, col;
printf("Enter elements in matrix of size %dx%d \n", ROW_SIZE, COL_SIZE);
/* Outer loop to iterate through each row */
for(row=0; row<ROW_SIZE; row++)
{
/* Inner loop to iterate through columns of each row */
for(col=0; col<COL_SIZE; col++)
{
/* Input element in array */
scanf("%d", &matrix[row][col]);
}
}
/*
* Print all elements of array
*/
printf("\nElements in matrix are: \n");
for(row=0; row<ROW_SIZE; row++)
{
for(col=0; col<COL_SIZE; col++)
{
printf("%d ", matrix[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Output –
Enter elements in matrix of size 4x3
10 20 30
40 50 60
70 80 90
100 110 120
Elements in matrix are:
10 20 30
40 50 60
70 80 90
100 110 120Example program to use three-dimensional array
/**
* C program to input and display three-dimensional array
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE1 2
#define SIZE2 2
#define SIZE3 3
int main()
{
int arr[SIZE1][SIZE2][SIZE3];
int i, j, k;
/*
* Input elements in array
*/
printf("Enter elements in three-dimensional array of size %dx%dx%d \n", SIZE1, SIZE2, SIZE3);
for(i = 0; i < SIZE1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < SIZE2; j++)
{
for (k = 0; k < SIZE3; k++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
/*
* Print elements of array
*/
printf("\nElements in three-dimensional array are: \n");
for(i = 0; i < SIZE1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < SIZE2; j++)
{
for (k = 0; k < SIZE3; k++)
{
printf("%d\n", arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}Output –
Enter elements in three-dimensional array of size 2x2x3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Elements in three-dimensional array are:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12Recommended matrix example programs
- Program to add two matrix.
- Program to subtract two matrix.
- Program to check matrix equality.
- Program to multiply two matrices.
- Program to find transpose of a matrix.
- Program to check identity matrix.
Practice more matrix programming exercises to learn more.
